Choosing The Best Augmented Reality Software Platform For Your Business
Article
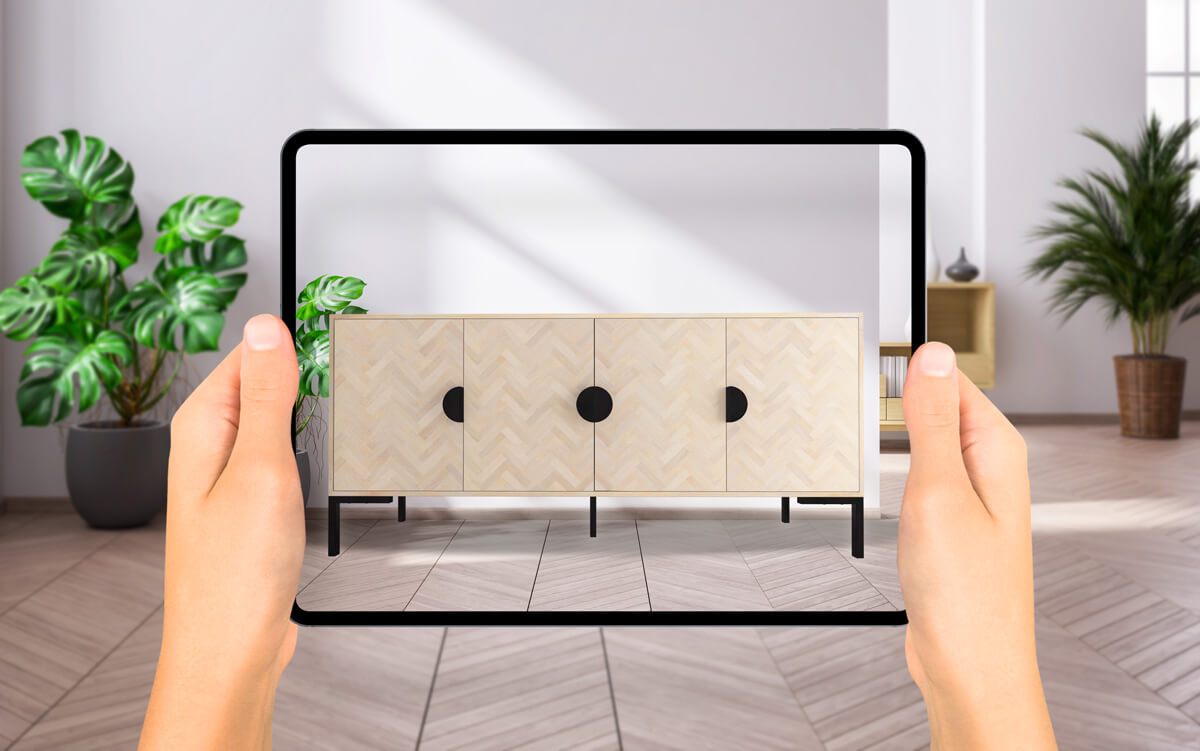

Part 1: What is Augmented Reality Software?
Did you know that nearly three-quarters of customers say they’d shop more often if retailers offered an AR experience.
Did you also know that less than of 52% retailers are using AR? This is an incredible opportunity for forward thinking retailers to get ahead of their competition.
It seems obvious that there is quite the opportunity on the table which, of course is why you are here, learning about augmented reality software.
The question is, what AR software should I choose to build my company’s first augmented reality experience?
We’re going to help you figure that one out. Let’s start nice and simple. Augmented reality (AR) is a bit like CGI (Computer Generated Imagery) in the movies, it overlays digital content over a camera view such as your mobile camera or webcam.
The augmented reality software understands the real world so that the virtual content looks like it’s actually there in the real world. AR responds in real-time, tracking the real world as you move.
What’s interesting about augmented reality is that for many of us, it’s still kind of a scary term.
Not in the way that AI is scary, but more in the way that many of us know what AR looks like because we have seen it in the movies or someone’s social post of a face filter but we don’t know how it works.
Not enough to explain it anyway so how do you know what the best augmented reality software is for what you want to do?
Most people’s first experience of AR was the massive game Pokemon Go.
Pokemon Go uses augmented reality software to understand and recognise the ground in the camera view. It can then overlay the Pokemon character so it looks like the character is really there in front of you. It then uses the sensors on the phone so when you move it still looks like its there in front of you.
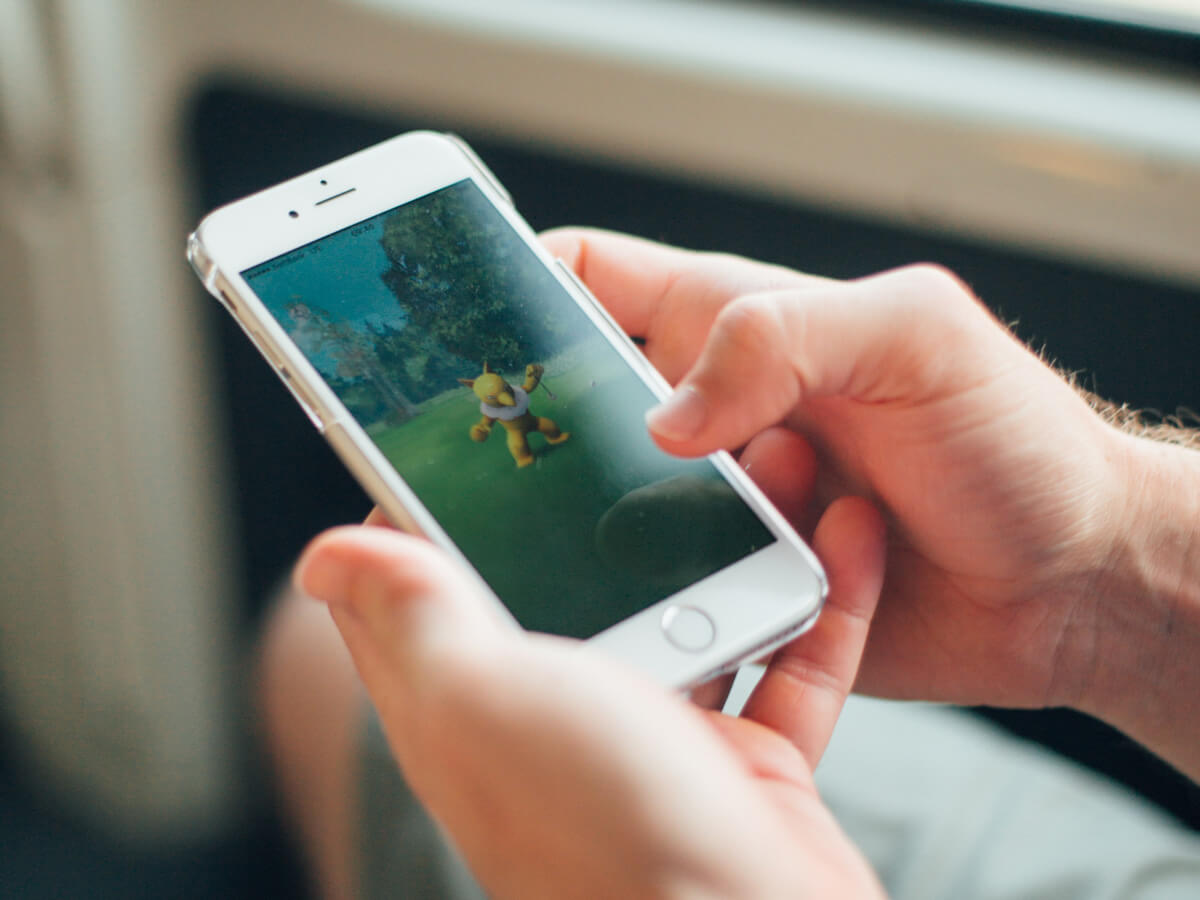

So no, augmented reality is not this frightening concept that lurks in the future. It’s here, it’s now, and it’s ready and waiting for you to jump in and build AR into your customer experience.
But get ready, because if you want to go on this adventure, you’re going to need an augmented reality toolkit or AR SDK.
What is Augmented Reality SDK?

It’s a bit of a mouthful, AR SDK stands for Augmented Reality Software Development Kit.
An AR SDK is the building block tool that allows software developers to build an AR app, it is kind of like the developer’s tool chest.
In an augmented reality SDK, you’ll find the tools that power things like:
- Image tracking
- Plane detection
- 3D object tracking
- Face tracking
- SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping)
AR SDKs typically come with documentation that describes what functions are available and what those functions do as well as an API (application programming interface) to connect to other third party services.
Though some augmented reality SDKs are usually for a single framework but some frameworks can work across on multiple.
Ok what’s an AR framework then, you ask?
An AR framework extends the SDK, the words are fairly interchangeable, an SDK is a set of software development tools used to create AR applications. An AR Framework is basically a platform which is used for developing software applications. It provides the necessary frame that holds the different building blocks together so applications can be developed.
There are many different frameworks and SDK’s that make AR apps that work on different operating systems and devices e.g a Windows laptop or Apple iPhone and these different frameworks and SDK’s do augmented reality in lots of different ways.
Ok so what are the different types of augmented reality ? Let’s take a look.
What are the different types of Augmented Reality?
Now that we are using the core tools and blocks within the frame now we can look at the different ways to trigger an augmented reality experience to start and how the AR app tracks the real world. As you can probably tell you can arrange the blocks in different ways but the main ones are:
- Plane Detection : Tapping a button to place the AR experience on the floor
- Image Tracking: Scanning a 2D image with the camera
- Face Tracking : Scanning a face with the camera
- SLAM : Scanning a 3D object or 3D environment such as a room interior
- Geo location : Being in a certain location
Let’s quickly review what each of these different types is capable of doing.
1. Plane Detection
You want to place digital content such as a 3D model of a piece of furniture in front of you in the real world and move it into place
2. Image Tracking
You want to overlay an image with digital content such as some product packaging or physical advertising like a catalogue or in-store signage
3. Face Tracking
Face tracking is used to overlay a face with digital content like a social platform filter or virtually trying on a pair of glasses or a hat
4. SLAM
This ones a bit tricky, essentially it’s using a 3D map to track the real world digital content, it could be a 3D map of a real world object like a piece of machinery to overlay safety instructions or or a collection of objects like an interior of a room.
5. Geo Location
Geo-Location triggers digital content to display when the device is within an area defined by GPS longitude and latitude. The experience then uses another type such as SLAM or Plane Detection to display the digital content. Geolocation is used for displaying information about a landmark as part of a tourism experience or finding where to go or even a game like Pokemon Go

So now, you’ve got a good handle of how Augmented Reality software is built up from an SDK and a framework that contains different ways to trigger and track the real-world to create an augmented reality experience.
In Part 2 we will then dive into the main categories of augmented reality experiences and how you work out what augmented reality software is best for what you want to achieve.
Part 2 : What Can Augmented Reality Tools Be Used For?
Let’s look at the main categories of augmented reality experiences and how you work out what augmented reality software is best for what you want to achieve.
Augmented reality is an enabling technology that can be applied across services, products, locations and much more. Social filters from Instagram and Snapchat and games like Pokemon Go or Nintendo Pikmin have massive engagement because they are great fun but Apple CEO Tim Cook says “I see AR as being profound. AR has the ability to amplify human performance.” and this breaks down to the utility that the AR experience provides. Let’s look more closely at what applications and use cases that Augmented reality is transforming today:
- Training
- Productivity
- Sales and Marketing
- Education
- Building Design & Construction
- Repair and maintenance
Training
Forward-thinking companies are now using AR solutions to train and onboard new employees.
This means that rather than death by PowerPoint, new employees can fully visualise them and even go through a few practice runs.
This is especially valuable in industries where there is a high risk to employee safety, minimising the risk of harm to themselves and their colleagues. Or where cost is a major factor such as medical training.
Productivity
Using AR-powered productivity apps, enterprises can improve employee efficiency across processes and workflows by delivering the right information at the right time. For example in pick and pack logistics AR glasses are being used to show the optimal path to complete the order and visually highlighting each shelf location.
Sales and Marketing
Augmented Reality platforms have opened up a world of opportunity for retailers.
For some time now we’ve been watching a huge trend toward online shopping, with almost a quarter of purchases currently taking place online.
It takes a leap of faith for customers to buy a physical product sight unseen This problem makes converting online shoppers difficult (88% of carts are abandoned before purchase) and drives product return rates for eCommerce purchases as high as 30%)
With augmented reality, these challenges can be solved starting with 3D models of products and creating interactive product experiences. These enable potential customers to first understand the product at every angle and see all of the options such as colour and size, then see how it fits in their own home or business. This gives them the confidence that they have found the right product for them and complete the purchase.
Education
Educators face a new challenge, gaining and holding students’ attention is increasingly difficult in a world where instant gratification is always a thumb click away. On top of this the traditional challenge of making it relevant to the students lives and the real world. We live in a 3D World but still present content in 2D – this is where augmented reality helps. It brings it to life through visually rich and engaging multimedia content such as seeing how the planets orbit in the solar system. It then goes further and makes the learning experience part of the real world like scanning plants to see what species it is. Augmented reality makes learning engaging, fun and therefore memorable.
Building Design & Construction
From the smallest interior to the largest skyscraper every project faces the same challenges of seeing what it should look like and communicating this to lots of different people. 3D and AR technology brings building professionals together enabling them to see how the pieces fit together and making it easier to make decisions speeding up the building process saving time, money and resources.
Maintenance & Field Service
The maintenance and service of machinery and infrastructure has a large impact on the bottom line of business as a failure of a part can cause a chain reaction of things to happen. Augmented Reality combined with sensors in the machines help to alert technicians before a failure and also complete the maintenance task. AR glasses can be used in repair and maintenance roles to project valuable data during the repair, such as required torque values or the location of various parts.
A Brief Guide to AR Development

Wondering how to program augmented reality?
AR development is a complex field, and we don’t have space to cover everything today (or, as a college professor of mine used to say “That’s outside the scope of today’s lecture”).
Instead, let’s look at a brief overview of AR programming in 10 broad steps.
1. Determine The Need
What is it that you need to program AR for?
What is the problem you want to solve? What do you need to communicate? How can you help your customers?
In short: What is your vision?
2. Describe your Vision
First without thinking too much, describe what you want to achieve and who you want to achieve it for. It’s your vision, be bold, you have the insights on what will be valuable to you but also the audience that you want to build this for. Keep your feet somewhat on the ground and keep it within a use case and break it down into use cases like one of the examples above.
3. Put a fence around it
Now it’s time to think of the things that will need to be considered. What’s the information that goes into it? Maybe it’s describing a process, maybe it’s bringing certain people together. Having some ballpark of a budget can help and a timeline even if it’s just the first phase all helps to make it happen.
4. Define it further
This is where you zoom a bit, get into the details of your build
- What will users be able to achieve by using it?
- What benefit does that bring to your business?
- What are your assumptions, do you need to prove anything first?
- What is the minimum viable product (MVP) for this build?
- Has anyone tried to solve this problem before?
You’d be wise here to check out your competitors and see what you can learn and create a point of difference
From there, you should ask the question: how can we do it better?
5. Find out who has the expertise
Someone is going to need to build the vision, right? But how do you decide who?
Maybe your business has people that can apply their knowledge. Look to your network and who can help you discover the right people.
But maybe, you’ll need to find the right people, which means a few more questions:
- Do you hire someone or do you outsource?
- What do these people need to have done to have the expertise needed?
- What are the key things that will help you choose between people?
6. What are things you will need to know to make decisions?
Now that you’ve found the right people, if you want to be the decision maker then you will need the knowledge to make the decision. Sometimes this is asking the right questions and goes back to what was defined in step 4.
Now an important part is understanding what a decision you’re making means and to do this you may need to take the time to learn. After all that is why it’s called making an informed decision and decisions often involve compromise so ask:
- Is there an alternative?
- Why is this option better than the other option
Having a plan saying what it is and what it will do and sometimes more importantly what it won’t do will keep everyone on the bus and moving towards the destination. This is called the scope of work.
7. Creating the Scope of Work for Augmented Reality
Whenever you’re collaborating with people inside or outside your organisation, it’s all too easy to miscommunicate or make presumptions that send a project off course. That’s why a scope of work (SOW) is an important document for any Augmented Reality project.
A SOW brings together everything from work details, to schedules, terms, and expected outcomes to not only define exactly what should be done on a project. But also to protect everyone from the dreaded scope creep where features, additions, and nice-to-haves balloon your project beyond what you’d initially planned.
Think of it like a map that guides the completion of the project, these are the must haves for any augmented reality scope of work.
- Detail: If it’s not on the SOW, don’t assume it will get done.
- Visualisation: Showing what you’re talking through pictures and storyboards go a long way in explaining your vision and also keeping your expectations in check.
- Definitions: Augmented Reality has many terms and phrases and making sure you and the team understand these is important. This goes back to knowing what you need to know and also making sure everything is defined within reason.
- Time for reviews: A SOW is a plan. But at their best, plans are just educated guesses. Make sure your timeline has space in it for reviews, as the reviews can often reveal things that mean a change in plan.
- What is success? Probably the most important aspect of an effective SOW is everyone understanding what success looks like. If it’s at all unclear what you want to achieve at the end, rewrite it.
Now a SOW can be a trap in itself, you can spend too much time and budget endlessly defining the scope. At some point you need to be comfortable that you have the plan in place and the right people to achieve it. The best thing to have understood is the augmented reality user experience or at least the augmented reality user journey and this is often defined by how the augmented reality experience triggers and tracks and this is defined by the augmented reality solution which can be called the augmented reality platform or the augmented reality toolkit or the augmented reality framework or the augmented reality SDK. Yes the pieces are all falling into place now right ! (If not then you got back to the start)
What is the best Augmented Reality Platform Framework Toolkit SDK ?
The best augmented reality toolkit platform toolkit platform framework SDK that we will just call the augmented reality solution is the one that achieves your vision. Maybe you’re the type of person that likes to work backwards and perhaps have jumped all the way up to here but let’s assume you have a vision and know what’s important to achieve that vision.
Let’s first start with the augmented reality SDK’s for mobile devices.
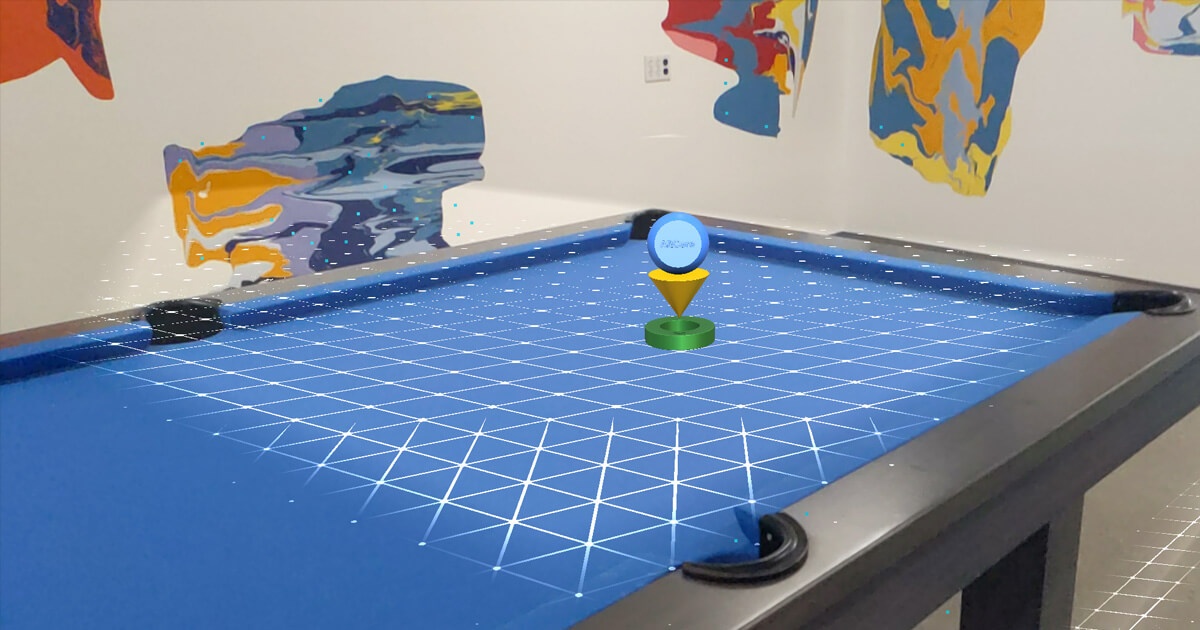
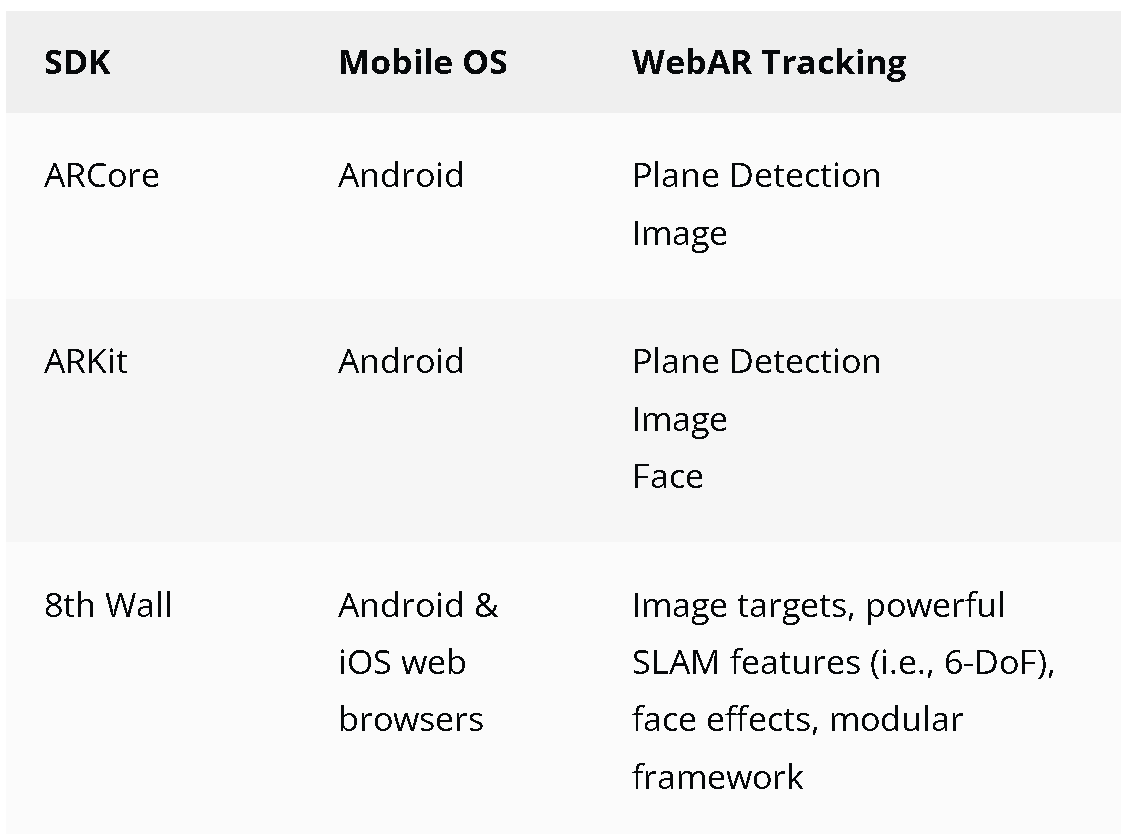
ARCore
ARCore is part of the Android operating system and therefore described as ‘native’. It can be used in a mobile app and also the web but of course there are differences. ARCore can power Plane Detection experiences and Image Tracking experiences. Because it’s built into the Android operating system used by many phone manufacturers and also available on the web it is extremely accessible and a good fit for Sales & Marketing experiences.

ARKit
ARKit is part of the iOS operating system on Apple devices such as the iPhone and iPad. Just like ARCore it can be used in a native app and on the web. ARKit powers Plane Detection and Image Tracking experiences but also Face Tracking experiences on the web.
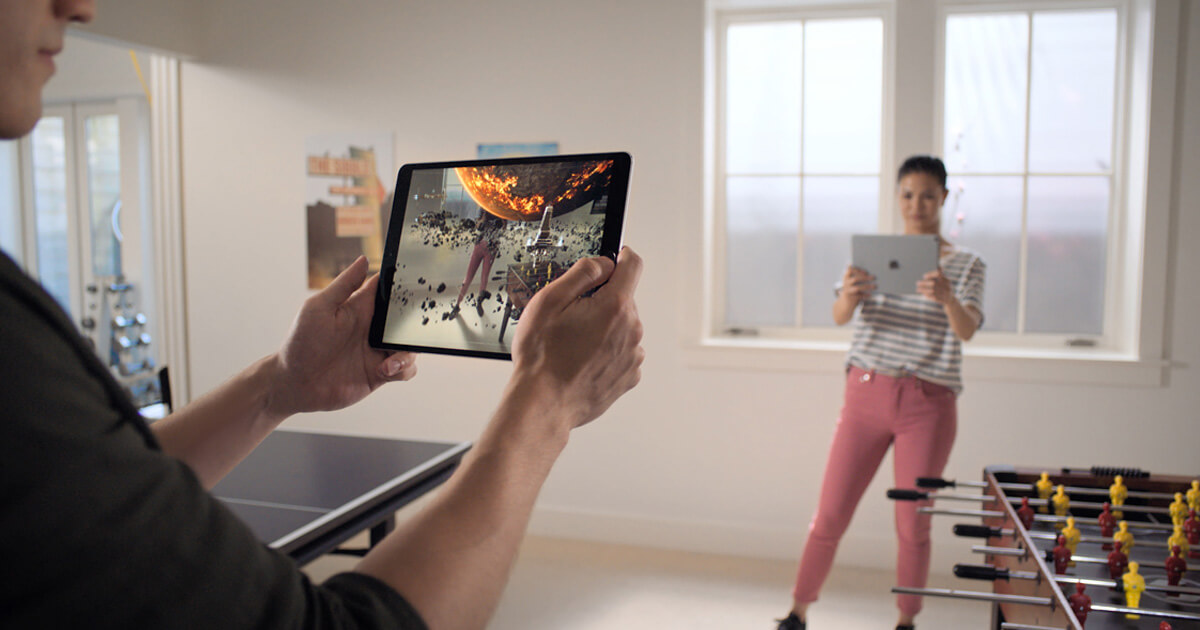

8th Wall
8th Wall is an web AR solution that works in browsers on both Android and iOS devices and therefore described as cross-platform. Now there are also platforms that use the native ARCore and ARKit technologies together with other technologies so you can concentrate on your vision rather than building your project twice so if you’re building if you want to take a shortcut then you might be more suited to choosing the best augmented reality platform available.
Plattar Solutions
Plattar is the augmented reality platform for product experiences. Plattar is the easiest platform for building, managing and deploying 3D and AR experiences across the entire customer journey.
- BUILD – Our intuitive no-code tools let creators build in 3D and AR with ease. Import assets, create simple product visualisations or complex product configurators in our easy-to-use Experience Builder.
- MANAGE – Manage 3D models, Product Feature Annotations, Product information and performance data – all from a single, powerful product visualisation platform. Plattar makes remote collaboration a breeze.
- PUBLISH – Deploy all your 3D and AR experiences with clicks. Automatically optimised for quality, performance and leading user experience across the web on all devices.
- Show customers how products will look and fit in their home or office.
- Virtually stock your whole range – connect your online and instore experience.
- Improve upselling by showing multiple products and combinations in a single view.
- Your entire range in 3D content can be leveraged across digital touchpoints.
- Let your customers virtually try-on or try-out products in 3D and AR
- Enable your customers to personalise, customise and configure your products.
Augmented Reality Platforms Summary
The best SDKs for programming from the ground up:
How You Can Incorporate Augmented Reality Software into Your Online Store
Before we close up shop for the day, let’s look at 4 ways you can incorporate AR experiences into your online store:
- 3D and AR product visualisation for eCommerce
- Immersive Product Presentations
- Virtual Product Try-on
- Business-to-business Sales
1.360-Degree 3D Products
The traditional approach to displaying products online is to use 2D photography.
Unfortunately, it doesn’t matter how many 2D photos you upload for each product, it will simply not be sufficient for customers to fully visualise a product.
This leads to mismatched expectations and a higher rate of order returns.
Leading online retailers can circumvent this challenge by investing in 3D product photography and visualisation, allowing shoppers to interact with a 360-degree versionof your product online.
2.AR Product Visualisation
One of the most powerful ways to use augmented reality in the eCommerce world is to provide a way for customers to visualise what your items will look like in the context of their own home or office.
Not only will buyers be able toNot only will buyers be able to confirm that products fit in a physical sense, but they’ll also be able to confirm that the products will work stylistically in their intended environment.
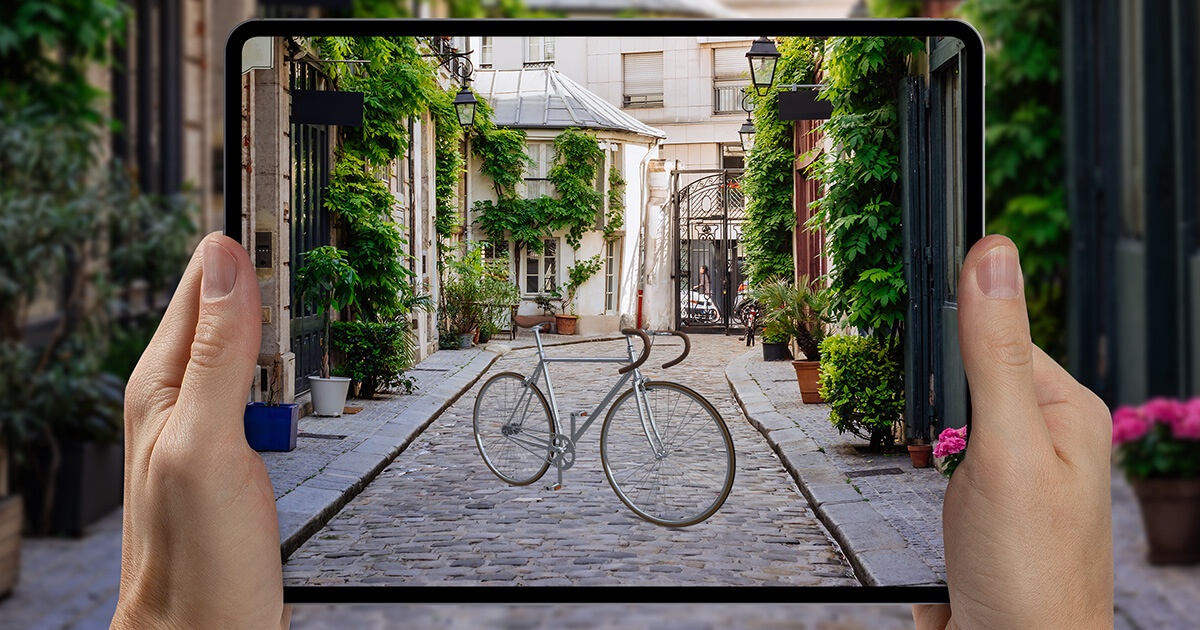

- Let people experience your products before they buy, all in 3D and Augmented Reality.
- Engage your customers where they are spending time on mobile and the web.
- Use the same content to create in store demos and virtual showrooms.
3. Virtual Stores
One of the major benefits of the eCommerce revolution is the ability to sell into distributed territories. No longer are retailers restricted to their physical environment.
However, an in-store experience is still preferable to many, but it’s not exactly practical for your customer in Australia to visit your sole shopfront in Colorado.
You can find a midway solution to this problem, however, by building a completely virtual store.
In this environment, shoppers can interact with a virtual environment (set up like a physical store rather than a typical eCommerce site), giving them almost the same experience as they would receive in your actual store.
This is especially effective for homeware stores, where multiple products are often displayed for use together.
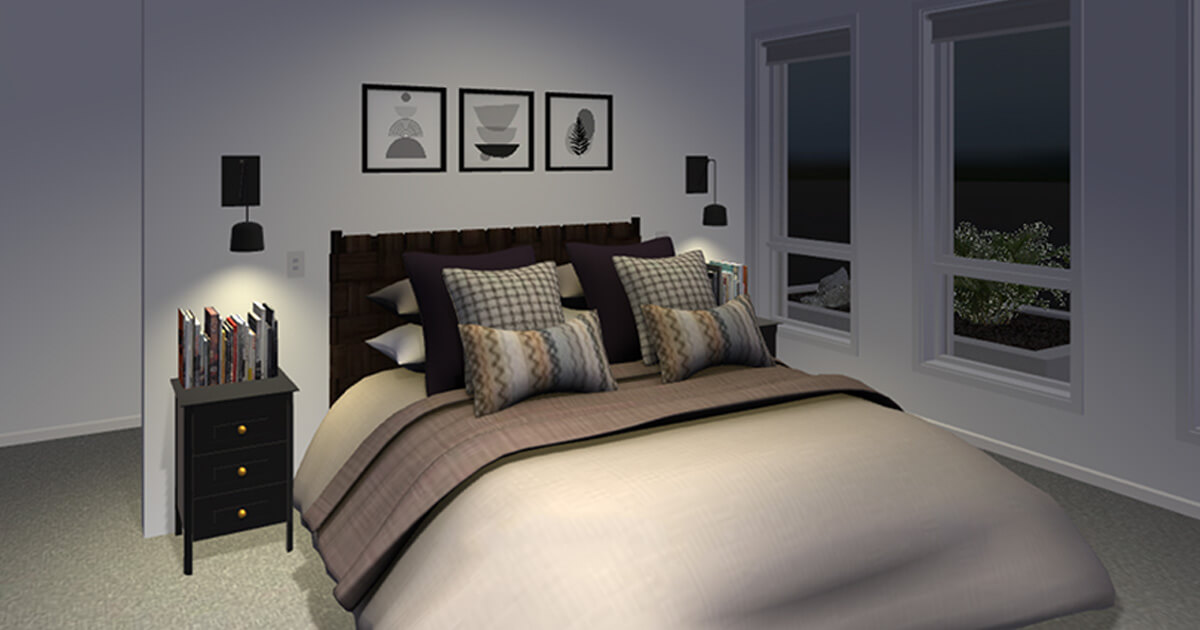

4. Complete Customisation
The fourth and final way that online retailers can leverage AR is by providing a high degree of personalisation and customisation of products.
Retailers offering highly customisable products can provide an AR experience that allows shoppers to see exactly what they’re ordering before it’s created for them.
Conclusion – Getting Started With Augmented Reality Software
Feeling confident about using AR software to create stunning and engaging experiences for your product range in 3D?
Let’s recap on the 10 steps to success in this domain:
- Determine The Need
- Create a Vision
- Designate your Developers
- Take a Course in AR Development
- Choose Your Augmented Reality Toolkit
- Get Familiar With How The Tool Works
- Design a Plan
- Build and Test
- Deploy
- Improve
Or, of course, if you’d rather keep focusing on your core business, and skip the whole development stage altogether…
Plattar is your end-to-end platform for bringing products to life online. Book a demo to see how we can help bring augmented reality experiences to your customers today.